Supplemental Figures
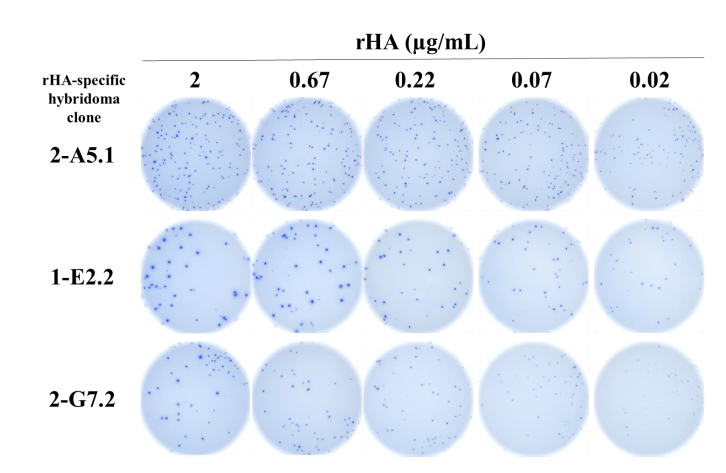
Supplementary Figure 1. Inverted ImmunoSpot® reveals differential mAb functional affinity for influenza hemagglutinin. Murine B cell hybridomas, each secreting monoclonal antibody (mAb) reactive with the hemagglutinin protein of influenza H1N1 vaccine strain (A/California/2009) (described previously [29]), were plated into wells coated with anti-mouse Ig capture antibody to generate individual secretory footprints. After removal of the cells, His-tagged recombinant hemagglutinin (rHA) was added to replicate wells at decreasing concentrations. Antigen-specific secretory footprints were then visualized using a biotinylated anti-His tag detection reagent, followed by addition of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated streptavidin, and subsequent enzymatic conversion of a precipitating substrate. As illustrated in the representative well images, secretory footprints from each of the B cell hybridoma lines were readily apparent using the highest concentration of rHA probe for their detection. However, the size (and density) and number of visible secretory footprints generated by each of the B cell hybridoma lines was reduced when limiting concentrations of the rHA probe were used for their detection. Based on the results of this experiment, the mAb secreted by the 2-A5.1 B cell hybridoma line has an increased functional affinity for the rHA probe compared to the mAb secreted by 2-G7.2.
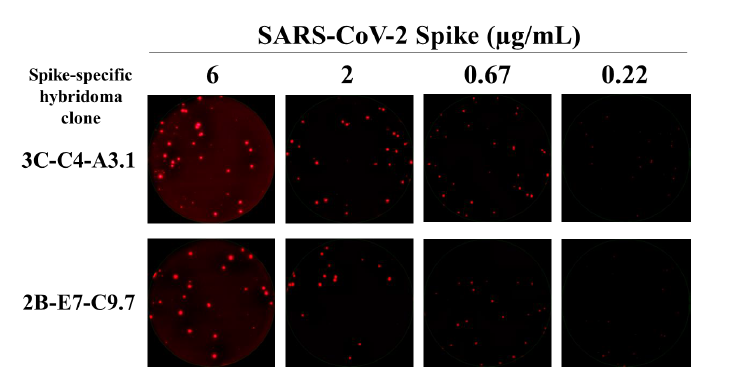
Supplementary Figure 2. Inverted ImmunoSpot® reveals differential mAb functional affinity for SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Murine B cell hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibody (mAb) reactive with the full-length Spike protein from the prototype Wuhan-Hu-1 strain of SARS-CoV-2 were plated into wells coated with anti-mouse Ig capture antibody to generate individual secretory footprints. After removal of the cells, His-tagged recombinant Spike protein was added to replicate wells at graded concentrations. Antigen-specific secretory footprints were then visualized using a biotinylated anti-His tag detection reagent, followed by addition of fluorescently-conjugated streptavidin. As illustrated in the representative well images, secretory footprints produced by both B cell hybridoma lines were readily apparent using the highest concentration of His-tagged Spike protein for their detection. However, the fluorescence intensity, size, and number of secretory footprints generated by each of the B cell hybridoma lines was reduced when limiting concentrations of the Spike probe were used for their detection.
